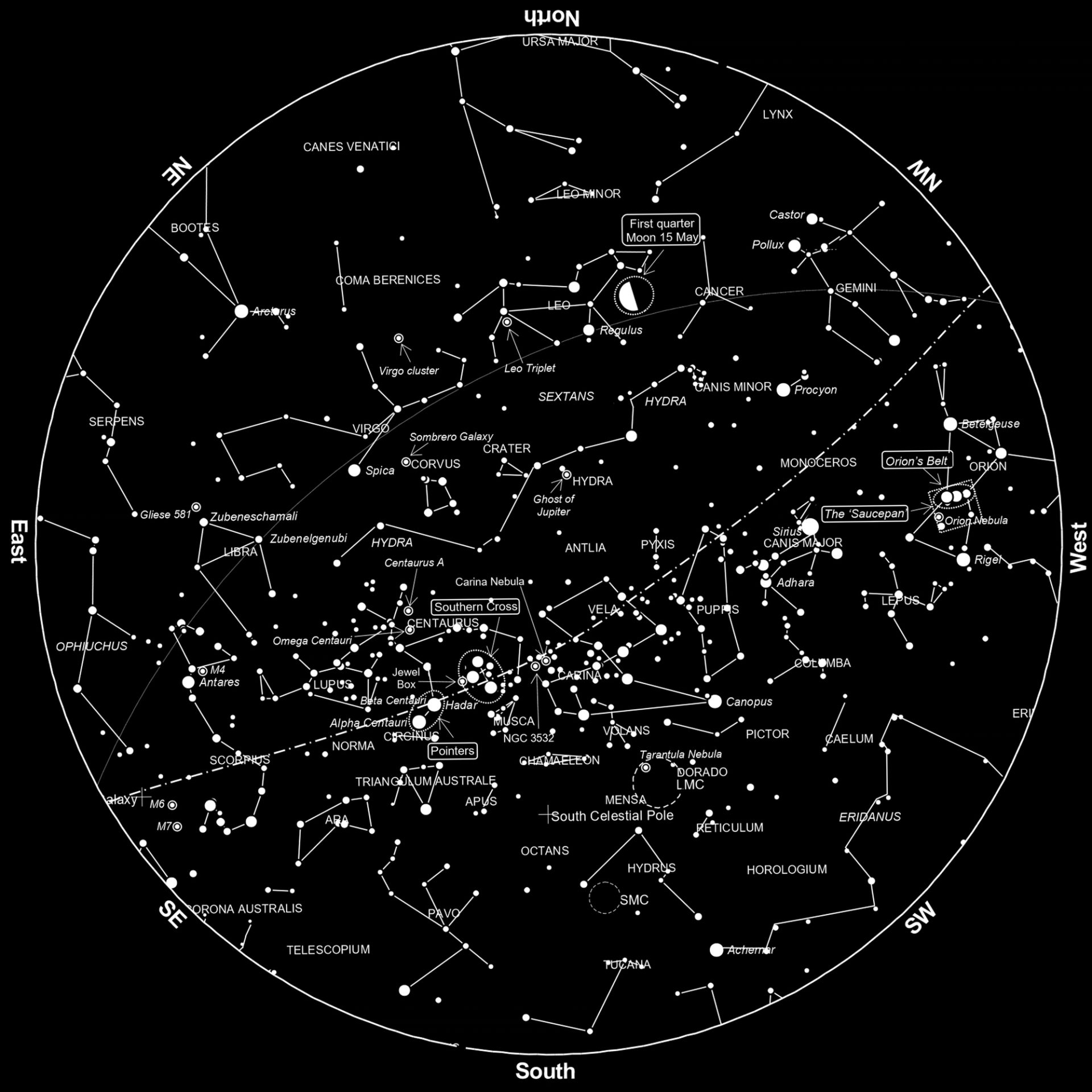
Sky Guide May 2024

‘The best time to observe any meteor shower is after midnight, usually a few hours before dawn, so on the mornings of the Monday 6 and Tuesday 7, look toward the east.’
Moon phases
Last quarter Wednesday 1 May 9:27 pm AEST
New Moon Wednesday 8 May 1:22 pm AEST
First quarter Wednesday 15 May 9:48 pm AEST
Full Moon Thursday 23 May 11:53 pm AEST
Last quarter Friday 31 May 3:13 am AEST
Planets
All the planetary action in May is in the morning sky. There are no planets visible in the early evening throughout the month.
Mercury is in the east, moving from Pisces to Aries, with a brief transit through Cetus, just after the middle of the month and then into Taurus at the end of the month. On 6 May, the crescent Moon is above and to the left or north of Mercury.