Sky Guide July 2025

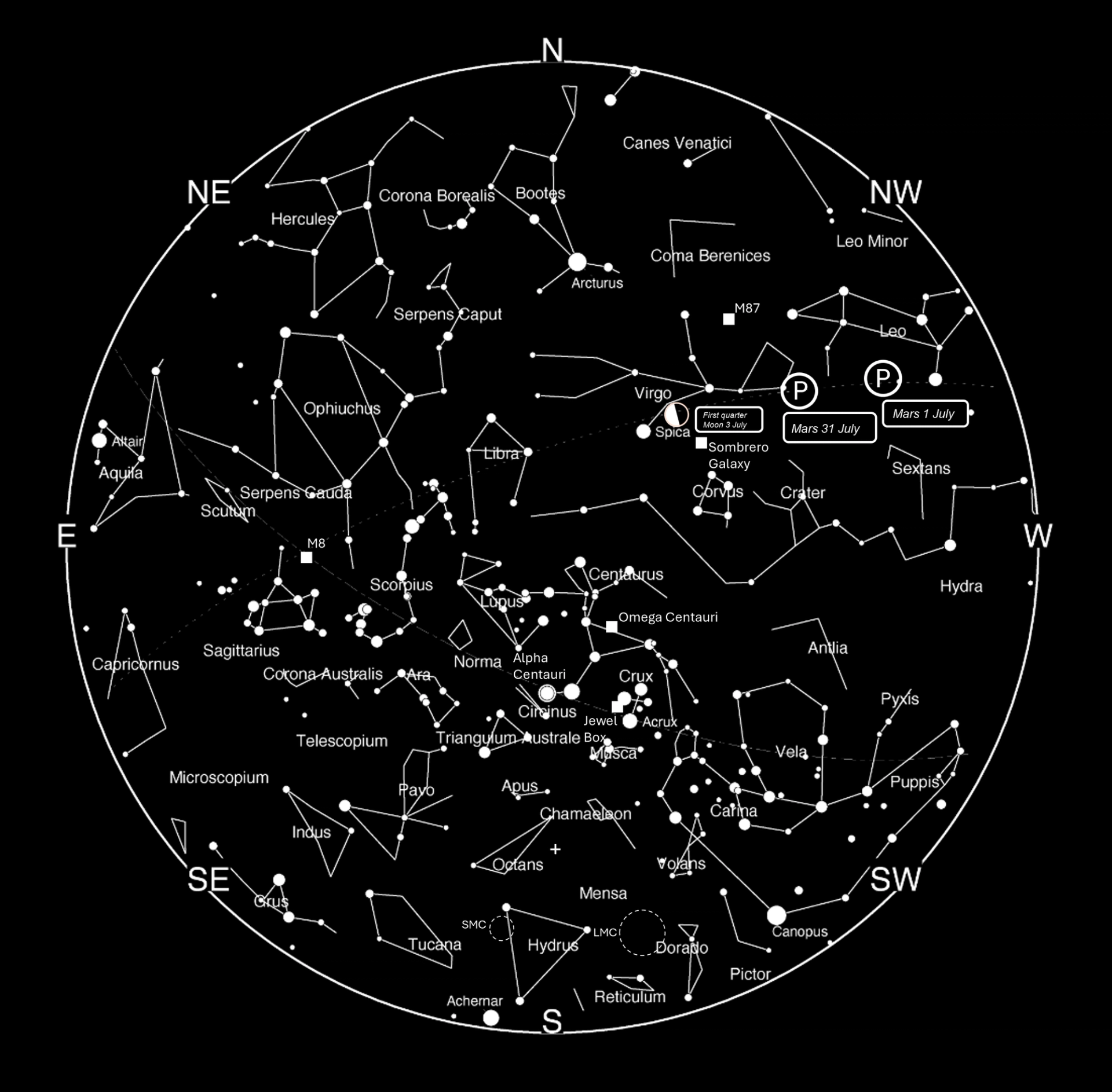
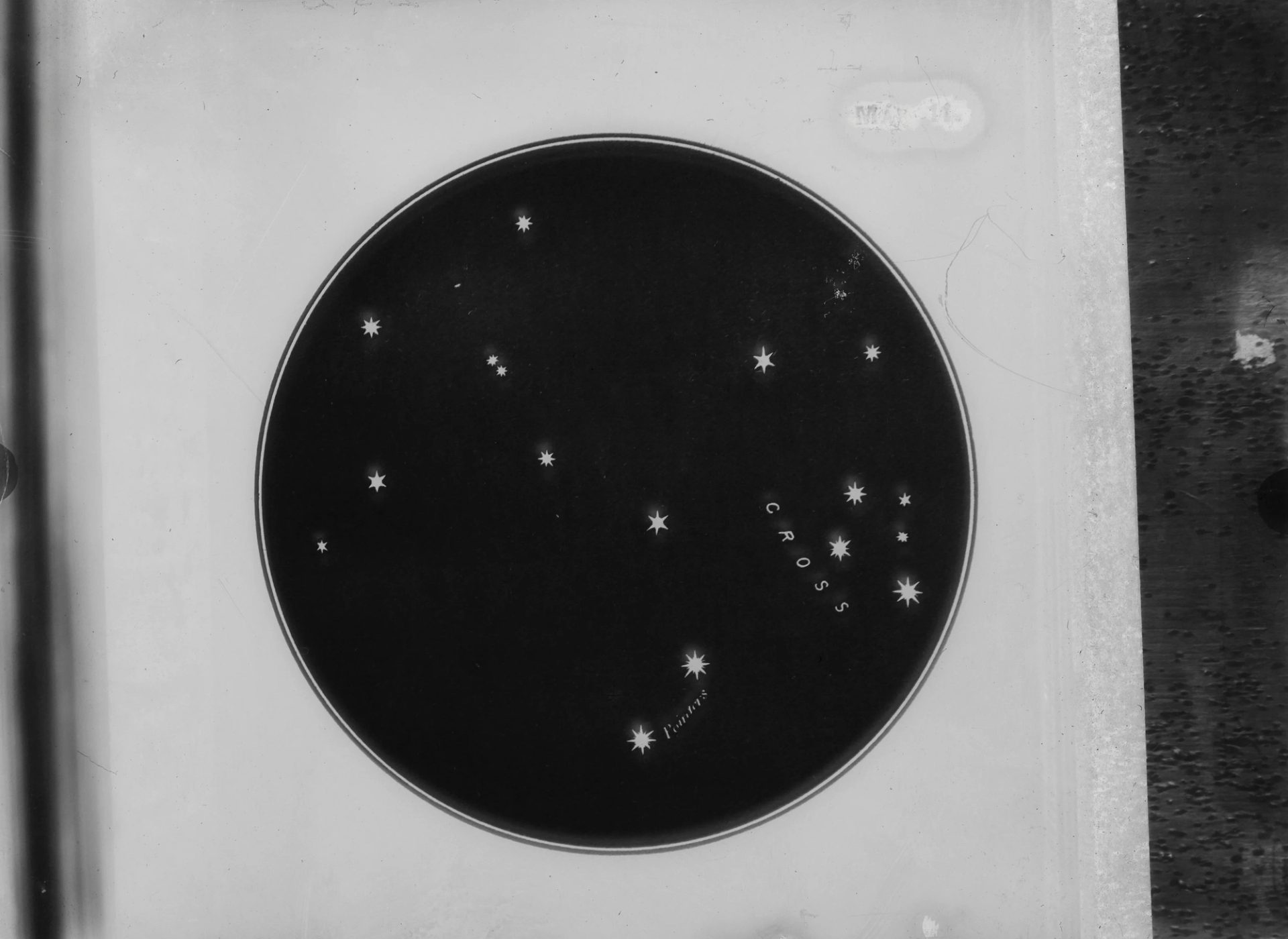
‘This month, the Southern Cross is particularly prominent, as it is almost vertical in the southern sky in the early evenings. Astronomers refer to it by the Latin name Crux and it is the smallest of the 88 constellations they recognise. It is this compactness that helps make it stand out.’
Moon Phases

First quarter – Thursday 3 July 5:30 am AEST
Full Moon – Friday 11 July 6:37 am AEST
Last quarter – Friday 18 July 10:38 am AEST
New Moon – Friday 25 July 5:11 am AEST
Planets

EVENING
As Mercury is lost late in the month, is left as the only evening planet.